Autoimmune diseases impact a significant portion of the population, with estimates indicating that around 50 million Americans are affected. Due to the complexities surrounding diagnosis, this number may be considerably underestimated. Alarmingly, autoimmunity is reaching epidemic proportions, with research suggesting annual increases of 3-12% in cases. This rise in prevalence underscores the need for more comprehensive approaches, such as functional medicine for autoimmune disease, which aims to identify and address root causes rather than just managing symptoms.
Functional medicine seeks to identify and address root causes of chronic diseases rather than focusing solely on managing symptoms. By considering factors like genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and lifestyle choices, functional medicine autoimmune practitioners create personalized treatment plans that can reduce chronic inflammation, improve gut health, and restore immune balance. This approach offers hope for those wondering, “Can functional medicine cure autoimmune disease?” while acknowledging that managing autoimmune diseases often requires ongoing care and lifestyle adjustments.
What Are Autoimmune Diseases?
Autoimmune diseases are a group of conditions where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, viewing them as foreign invaders. This can result in chronic inflammation, pain, and damage to organs and tissues. While traditional treatments often include medications like thyroid medication (e.g., levothyroxine) for thyroid disorders or DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis, functional medicine methods go deeper, examining potential triggers and imbalances.
Causes of Autoimmune Disease
Functional medicine practitioners believe that autoimmune diseases result from a combination of factors rather than a single cause. By understanding the various contributors, patients can better manage their conditions through a more holistic autoimmune treatment approach.
Genetics
Genetic predisposition can increase the likelihood of developing autoimmune diseases, yet genetics alone rarely cause them. Functional medicine emphasizes that genetics load the gun, but lifestyle and environmental factors pull the trigger. With root cause analysis, functional medicine practitioners assess whether specific genetic markers may influence immune system function and which personalized interventions, such as stress management or diet, could help counteract genetic susceptibility.
Environmental Exposures
Environmental exposures to toxins, pollutants, or even personal care products containing harmful chemicals can disrupt immune function. In functional medicine, practitioners assess environmental triggers like toxin exposure and mold/mycotoxins, which are known to heighten immune reactivity and possibly trigger autoimmune responses. Cleaner swaps for household and personal care products are often recommended to reduce exposure to these environmental toxins.
Stress
Chronic stress disrupts immune function and can exacerbate autoimmune conditions. Functional medicine practitioners focus on stress management techniques like meditation, exercise, and vagus nerve activation to help regulate the nervous system and mitigate stress-induced inflammation. Adrenocortex stress profiles may be used to understand adrenal function and its impact on immune health.
Infections
Infections are known triggers for autoimmune diseases, with some viruses, such as Epstein-Barr, implicated in conditions like lupus and multiple sclerosis. Functional medicine practitioners may conduct infections panels to identify underlying infections that could be contributing to immune dysregulation. Strategies like immune system dysregulation repair and targeted supplementation help fortify the body’s defenses against infections that might trigger autoimmunity.
Immune System Dysregulation
Autoimmune diseases stem from an imbalanced immune system that fails to distinguish between harmful invaders and the body’s own tissues. Functional medicine focuses on restoring immune balance through root cause analysis and improving regulatory T cells that help keep the immune system in check.
Gut Problems
Gut health is central to immune health. Functional medicine autoimmune approaches often highlight the gut’s role in autoimmunity. Conditions like intestinal permeability (also known as leaky gut) and dysbiosis can allow harmful substances to enter the bloodstream, triggering immune responses. Functional stool tests and comprehensive stool tests assess gut health, including microbiome balance, and practitioners may suggest probiotic supplementation and anti-inflammatory diets to improve gut health.
Signs and Symptoms of Autoimmune Disease
Autoimmune diseases manifest in various symptoms depending on the specific organs and tissues affected. Common signs include chronic inflammation, joint pain, skin rashes, digestive issues, and cognitive abilities changes like brain fog. Functional medicine practitioners often recommend omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and curcumin for their anti-inflammatory properties.
5 Common Autoimmune Diseases in the United States
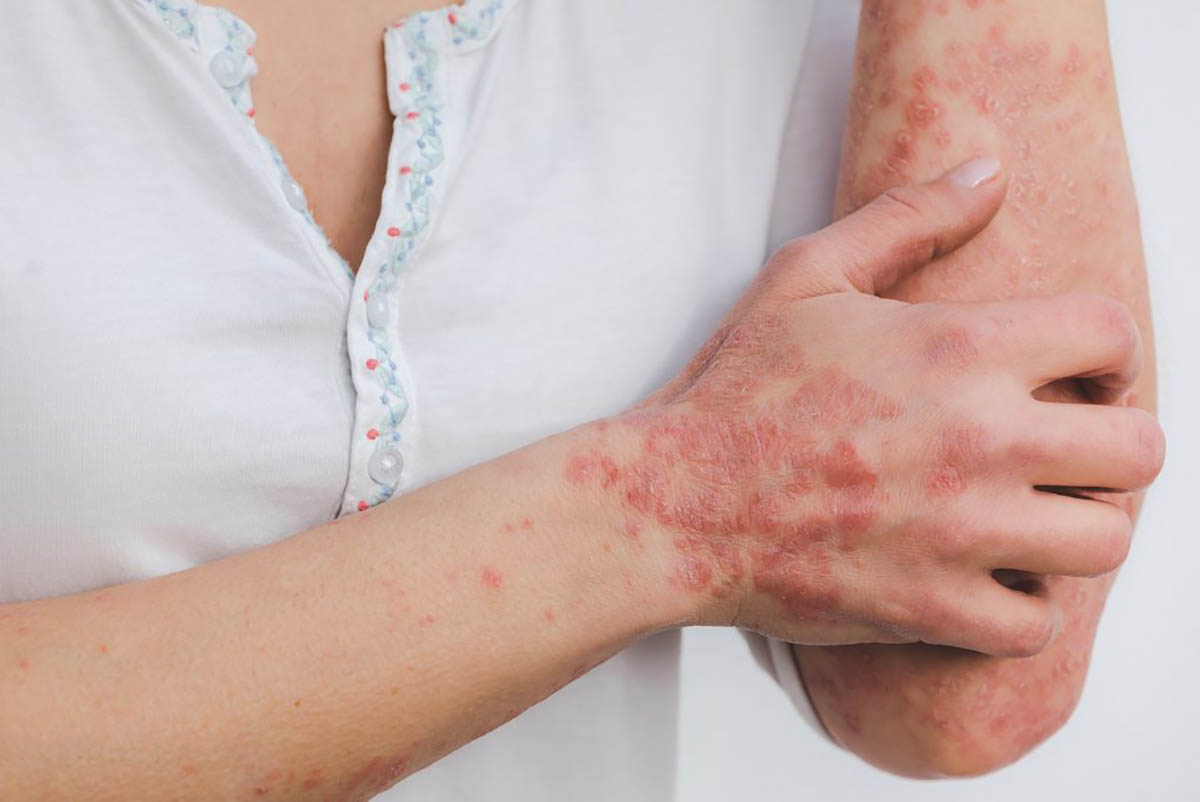
Autoimmune diseases are prevalent in the U.S., with several conditions affecting millions of people and significantly impacting their quality of life.
1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most widespread autoimmune diseases, affecting joint health and causing persistent inflammation. In 2020, approximately 17.6 million people worldwide were estimated to have RA (with a 95% uncertainty range of 15.8–20.3 million). This high prevalence highlights the global impact of RA and the demand for effective management strategies. While traditional treatments like DMARDs and biologic drugs target symptom relief, functional medicine for autoimmune focuses on underlying causes, potentially offering more sustainable relief.
2. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune thyroid disorder, leads to an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), with symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and cold sensitivity. Functional medicine often includes thyroid panel testing (including TPO and TG antibodies) to assess the extent of immune involvement. Practitioners may suggest selenium and vitamin D supplementation alongside dietary changes to support thyroid health and immune balance.
3. Celiac Disease
In celiac disease, the immune system reacts to gluten, causing damage to the small intestine. It can lead to digestive issues, nutrient deficiencies, and increased risk of other autoimmune conditions. Functional medicine practitioners may recommend an elimination diet and personalized dietary interventions to identify food triggers and heal intestinal hyperpermeability that often accompanies celiac disease.
4. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin condition marked by rapid cell turnover, leading to scales and red patches. It can also cause joint pain (psoriatic arthritis) in some individuals. Functional medicine autoimmune approaches focus on reducing chronic inflammation through an anti-inflammatory diet and addressing dysbiosis in the gut, as gut health is strongly linked to skin health.
5. Graves’ Disease
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune condition causing an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). Symptoms include anxiety, tremors, and weight loss. While conventional treatments may involve immune system suppression and thyroid medication like levothyroxine, functional medicine practitioners emphasize the importance of identifying molecular mimicry triggers that may provoke immune reactions.
How Functional Medicine Works for Autoimmune Diseases
Functional medicine practitioners adopt a unique approach to autoimmune diseases by focusing on root cause analysis rather than simply managing symptoms. This includes testing, holistic autoimmune treatment, and personalized care plans.
Functional Medicine Lab Tests for Autoimmune Disease
Functional medicine employs various lab tests to gain insight into underlying issues that may contribute to autoimmune disease development.
Screening Tests
Screening tests, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), c-reactive protein (CRP), and rheumatoid factor (RF), help assess inflammation and immune activity. For autoimmune thyroid conditions, a thyroid panel with TPO and TG antibodies offers valuable information.
Comprehensive Stool Test
A comprehensive stool test evaluates the gut microbiome, intestinal permeability, and signs of dysbiosis. Stool analysis may reveal imbalances, infections, or inflammation that could contribute to autoimmune disease progression.
Infections
Functional medicine practitioners assess infections like Epstein-Barr, which are often associated with autoimmune conditions. Addressing latent infections is crucial to reducing immune overactivity.
Adrenal Testing
The adrenocortex stress profile measures cortisol and DHEA levels, which are affected by chronic stress and can lead to immune dysfunction.
Autoantibody Testing
Autoantibodies like anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) and anti-nuclear cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) help diagnose autoimmune diseases and monitor their progression.
Sleep Study
Poor sleep quality is associated with worsened immune function. Functional medicine practitioners may recommend sleep studies and stress management techniques to support immune balance.
Cardiometabolic Panel
This panel checks for metabolic issues related to inflammation, such as insulin resistance, blood lipid abnormalities, and other indicators of cardiovascular risk.
Functional Medicine Treatments for Autoimmune Diseases
Functional medicine treatments focus on reducing inflammation, improving gut health, and addressing the environmental and lifestyle factors that trigger autoimmune responses.
Dietary Changes
Nutrient-rich diets, such as the anti-inflammatory diet or autoimmune paleo diet, aim to reduce chronic inflammation and support gut health. An elimination diet can help identify food sensitivities that may trigger immune responses.
Supplements
Functional medicine practitioners often recommend omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin with piperine for enhanced absorption, b vitamins, vitamin D, zinc, and glutathione to support immune health and reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle Modifications
Stress management techniques, vagus nerve activation, regular physical activity, and sleep optimization are critical for maintaining immune balance.
Why Choose Functional Medicine for Autoimmune Disease?
For patients in Tulsa or elsewhere seeking functional medicine in Tulsa or beyond, this approach provides a personalized, direct primary care model that addresses the root causes of autoimmune diseases. Functional medicine practitioners look beyond traditional treatments, emphasizing lifestyle and dietary changes that align with each patient’s unique genetic makeup and environment.
How to Find a Functional Medicine Practitioner
Functional medicine practitioners are certified by organizations like the Institute for Functional Medicine. Whether seeking functional medicine in Tulsa or other areas, patients can find qualified practitioners who offer both in-person and virtual care options.
At Vitality Functional Family Medicine, we are dedicated to providing a compassionate, personalized approach to managing autoimmune diseases through functional medicine. Understanding that each patient is unique, we focus on uncovering the root causes of immune imbalances rather than just treating symptoms. By addressing factors such as chronic inflammation, gut health, and environmental triggers, our team creates comprehensive, individualized care plans that promote long-term wellness and improved quality of life. Located in Tulsa, we offer a holistic, patient-centered approach that empowers individuals to take charge of their health and find lasting relief.
Conclusion
Functional medicine for autoimmune disease offers a comprehensive approach by focusing on root causes, dietary interventions, and lifestyle modifications. By addressing triggers and supporting the immune system, functional medicine provides hope for those seeking lasting solutions for autoimmune conditions.
FAQs
Can functional medicine help with autoimmune disease?
Yes, functional medicine can improve autoimmune disease management by addressing underlying factors, such as dysbiosis, environmental exposures, and chronic inflammation. This approach aims to improve symptoms and enhance the body’s natural resilience.
What is the best supplement for autoimmune disease?
Supplements like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and curcumin are commonly used to support immune health and reduce inflammation. The best supplements vary based on individual needs and should be discussed with a functional medicine practitioner.
What is the root cause of autoimmune disease?
Autoimmune diseases typically arise from a combination of factors, including genetic makeup, environmental toxins, chronic stress, and immune system dysregulation. Addressing these root causes is essential for effective management.

